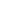|
|
 A
green carpet of garden runs from the main gateway to the foot of the
Taj. In essence, it is a Persian garden, a from born and nursed to
maturity in the desert flat of Persia. Such gardens were introduced to
India by Baber, the first mughal emperor, who also brought with him the
Persian infatuation with flowers and fruit, birds and leaves, symmetry
and delicacy. Unlike other Oriental gardens - especially those of the
Japanese, who learned to accentuate existing resources rather than
formalise them - the Persian garden was artificially contrived,
unbashedly man-made, based on geometric arrangements of nature without
any attempt at a "natural" look.
A
green carpet of garden runs from the main gateway to the foot of the
Taj. In essence, it is a Persian garden, a from born and nursed to
maturity in the desert flat of Persia. Such gardens were introduced to
India by Baber, the first mughal emperor, who also brought with him the
Persian infatuation with flowers and fruit, birds and leaves, symmetry
and delicacy. Unlike other Oriental gardens - especially those of the
Japanese, who learned to accentuate existing resources rather than
formalise them - the Persian garden was artificially contrived,
unbashedly man-made, based on geometric arrangements of nature without
any attempt at a "natural" look. Like Persian gardeners, landscape artists at the Taj attempted to translate the perfection of heaven into terrestrial terms by following certain formulas. In Islam, four is the holiest of all numbers - most arrangements of the Taj are based on that number or its multiples - and the gardens were thus laid out in the quadrate plan. Two marble canals studded with fountains and lined with cypress trees (symbolising death) cross in the centre of the garden dividing it into four equal squares. The mausoleum, instead of occupying the central point (like most mughal mausoleums), stands majestically at the north end just above the river. Each of the four quarters of the garden have again been sub-divided into sixteen flower beds by stone-paved raised pathways. At the centre of the garden, halfway between the tomb and the gateway, stands a raised marble lotus-tank with a cusped and trefoiled border. The tank has been arranged to perfectly reflect the Taj in its waters.
A clear, unobstructed view of the mausoleum is available from any spot in the garden. Fountains and solemn rows of cypress trees only adorn the north-south water canal, lest the attention of the viewer would be diverted to the sides !! This shows how carefully the aesthetic effect of the water devices and the garden were calculated. The deep green cypress trees with their slender rising shapes and curving topmost crests are mirrored in the water while between their dark reflections shines the beauty of the immortal Taj.
The Water Devices
The architect who was fully aware of the unaesthetic appearance of the grotesque pur-ramps and crude conduits, designed a clever system to procure water for the Taj through underground pipes.
 Water
was drawn from the river by a series of purs (manual system of drawing
water from a water body using a rope and bucket pulled by bullocks) and
was brought through a broad water channel into an oblong storage tank of
great dimensions. It was again raised by a series of thirteen purs
worked by bullocks. Except for the ramps, the other features of the
whole water system have survived. An over-head water-channel supported
on massive arches carried water into another storage tank of still
greater dimensions. Water was finally raised by means of fourteen purs
and passed into a channel which filled three supply tanks, the last of
which had pipe mouths in its eastern wall. The pipes descended below and
after travelling underground crossed into the Taj enclosure. One pipe
line runs directly towards the mosque to supply the fountains in the
tanks on the red sandstone plinth below the marble structure. Copper
pipes were used for separate series of fountains in the north-south
canal, lotus pond and the canal around it.
Water
was drawn from the river by a series of purs (manual system of drawing
water from a water body using a rope and bucket pulled by bullocks) and
was brought through a broad water channel into an oblong storage tank of
great dimensions. It was again raised by a series of thirteen purs
worked by bullocks. Except for the ramps, the other features of the
whole water system have survived. An over-head water-channel supported
on massive arches carried water into another storage tank of still
greater dimensions. Water was finally raised by means of fourteen purs
and passed into a channel which filled three supply tanks, the last of
which had pipe mouths in its eastern wall. The pipes descended below and
after travelling underground crossed into the Taj enclosure. One pipe
line runs directly towards the mosque to supply the fountains in the
tanks on the red sandstone plinth below the marble structure. Copper
pipes were used for separate series of fountains in the north-south
canal, lotus pond and the canal around it.An ingenious method was devised to ensure uniform and undiminished water pressure in the fountains, irrespective of the distance and the outflow of water. The fountain pipes were not connected directly with the copper pipes feeding them as this would have resulted in a gradual decrease in the volume and pressure of the water. Instead, a copper pot has been provided under each fountain pipe - which was thus connected to with the water supply only through the pot. Water first fills the pot and then only rises simultaneously in the fountains. The fountains are thus controlled by pressure in the pots and not pressure in the main pipe. As the pressure in the pots is uniformly distributed all the time, it ensures equal supply of water at the same rate in all the fountains. It is really creditable that the planner spared no efforts - belonging to art, architecture and engineering - to create a perfect production without the slightest weakness, architectural or aesthetic.The main supply of the water was however obtained through earthenware pipes. One such main was discovered under the bed of the western canal. The pipe is 9" in diameter and has been embedded in masonry at a depth of 5 feet below the level of the paved walk. Evidently, the mughal water expert was a master of his art and successfully worked out the levels in relation to the volume of water to ensure its unobstructed supply for centuries. He anticipated no repair work and therefore made no provision for it; hence the extraordinary depth at which the pipe was sunk.
The garden is irrigated by the overflowing of canals. The north-south canal has inlets of water through fountains. The east-west received its water through an interconnection with the north-south canal. Thus the quarters near the canals received an adequate supply of water and could be used for growing flower-plants which would not obscure the general view, while the distant quarters got a smaller supply of water and were suitable only for tall trees .